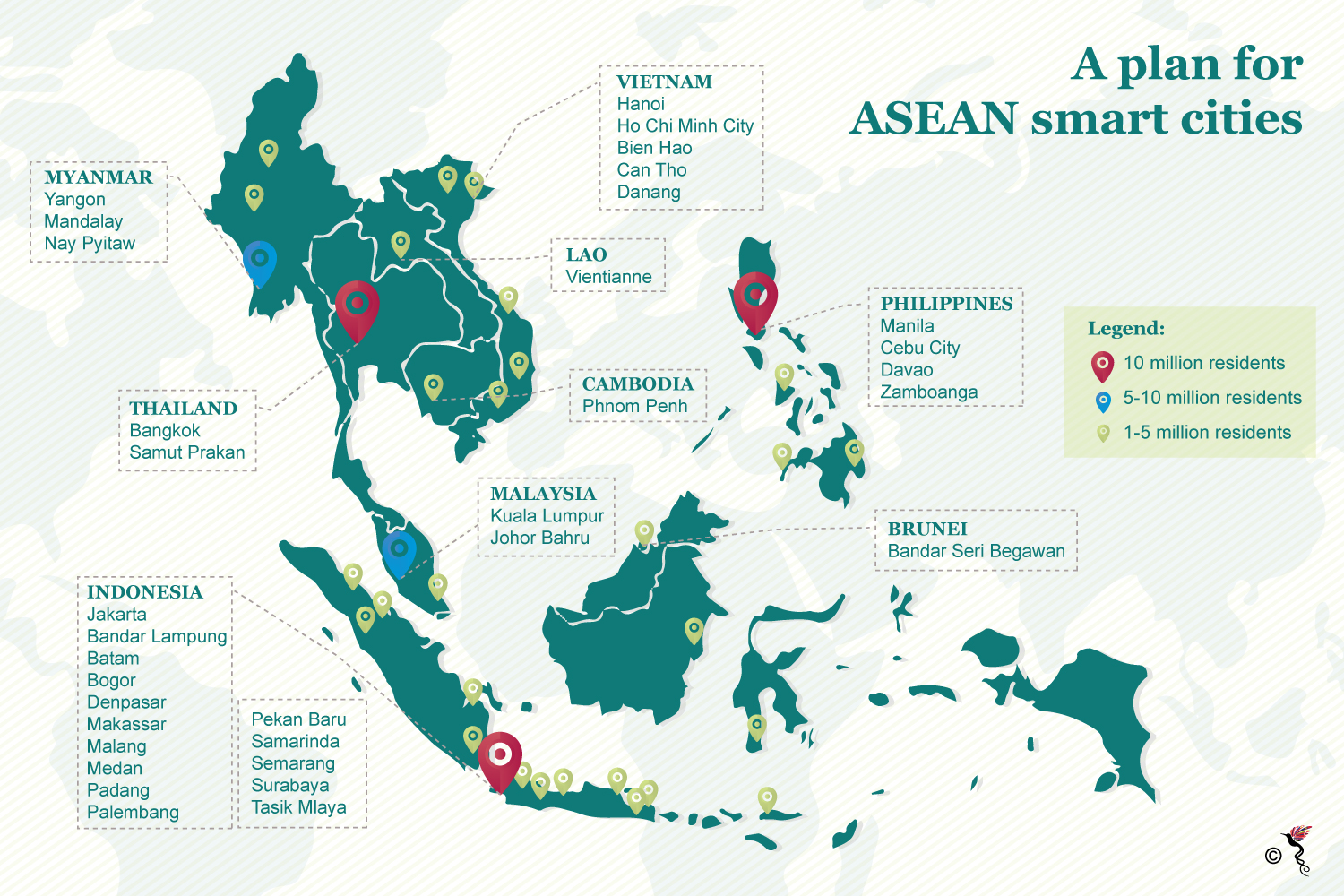
The ASEAN (Association of Southeast Nations) market – which combines Thailand, Cambodia, Myanmar, Malaysia, Indonesia, Lao, Vietnam, the Philippines, Singapore and Brunei – is one of the world’s fastest growing markets that is going through rapid urbanisation over recent years. ASEAN's total population is estimated to increase to 717 million by 2030 from 633 million in 2015, while more than half of them are under the age of 30.
As the rate of urbanisation increases, the demand for an integrated and modern infrastructure, efficient urban services and green spaces in the major cities within Southeast Asia will also rise. The United Nations predicted that continued population growth and urbanisation are projected to add 2.5 billion people to the world’s urban population by 2050, with nearly 90 percent of the increase concentrated in Asia and Africa. The world is also projected to have 41 megacities with more than 10 million inhabitants by 2030. Several decades ago, most of the world’s largest urban agglomerations were found in the most developed regions, but today, large cities are concentrated in the Global South – a more favourable term that is used to describe the "Third World" or "Developing World". The fastest-growing urban agglomerations are medium-sized cities and cities with less than one million inhabitants located in Asia and Africa.
The rapid growth in urbanisation is creating opportunities for ASEAN countries to make investments in infrastructure development, transportation and smart home projects across various cities within the region. This was to ensure that each level of the society can live better with high quality healthcare facilities, greener environment, secure housing equipped with modern basic amenities as well as convenient leisure facilities. The PwC (PricewaterhouseCoopers) in its Global Annual Review forecasted that the infrastructure investment needs of Southeast Asian countries for the 2010-2020 period are estimated at almost 600 billion dollars.
According to the Central Bank of Malaysia in its 2012 Annual Report, Asia is experiencing a growth in its urbanisation rates. By 2025, over two billion people in Asia, which accounts for half of the world’s urban population, are expected to reside in cities. This development is expected to contribute to the regional economic development and growth. According to a report by the Martin Property Institute, the urban population may grow by another 100 million to a total of 373 million people by 2030 from 280 million people today.
What is a smart city?
A smart city is sustainable urban development that integrates ICTs (information and communication technologies), natural resources and advanced technologies to manage the city's assets. The objective of a smart city is to provide smart urban homes with advanced facilities that are aimed to bring modern lifestyles to the population. According to the UNCTAD (United Nations Conference on Trade and Development), "a smart and sustainable city is an innovative city that uses ICTs and other means to improve the quality of life, efficiency of urban operation and services and competitiveness, while ensuring that it meets the needs of present and future generations with respect to economic, social and environmental aspects".
Source: A.T. Kearney
Environmental improvement
Smart homes are integrated with intelligent building and environmental improvement system that will recycle, reduce wastages and save electricity. For example, rain water is harvested and used for energy purposes while waste waters are treated and reused. This will lead to lower utility bills. The implementation of smart building solution will assist in saving water and energy usages as well as reducing the maintenance costs.
Information Technology
Smart homes are also deployed with the IoT (Internet of Things) technology like could computing and analytics, security and surveillance as well as disaster management system. These features play a role in creating a secure and safer living environment.
Growth of Innovation
A smart city is a well-planned development that could spur local economic development while improving productivity and services. It contributes to the innovation of smart mobility, education, retail and logistic, finance, building and living, tourism, leisure and health.
ASEAN countries are moving their value chain to be on par with the developed economies in the West. Many innovative initiatives have been taken by these countries to improve their competitiveness and productivity in the global market. At the same time, smart city development is not something new in the region as Singapore is one of the pioneer in this field. Other countries in the region like Malaysia, Indonesia, Thailand and the Philippines are also taking similar initiatives to create well-planned and integrated cities. These countries are emulating the western countries in an effort to provide a well-integrated development for the benefit of the people and the nation.
