Technology today is widely associated with the digital realm - computers, the internet, mobile device, and smartphones, - just to name a few, which has seen the mushrooming of a myriad of tech startups. However, technological innovation may not translate to definite technological progress. For example, Uber-fication has seen similar applications based on the ride-sharing giant’s model in various other industries like hospitality, healthcare and personal services. Its impact, while revolutionary from an economic and social standpoint, doesn’t fundamentally affect any change in a technological sense.
As opposed to just disrupting existing business models, engineering technological progress at a fundamental level, using previously theoretical scientific discoveries for real-world applications will likely take humanity to the next paradigm shift in technology. The term for such a phenomenon, is deep tech. While it is completely understandable to be wary of anything with the prefix “deep” (think deep web and deep state), deep tech is characteristic of actual scientific progress in engineering unique, often patent protected, next generation technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), genome editing, advanced facial recognition and robotics.
Around the world, deep tech startups are already starting to make waves in the healthcare, agriculture, bio-robotics and energy sectors. Within Southeast Asia, such startups are still at a nascent stage of development but are nevertheless working hard to bring experimental technology to day-to-day use.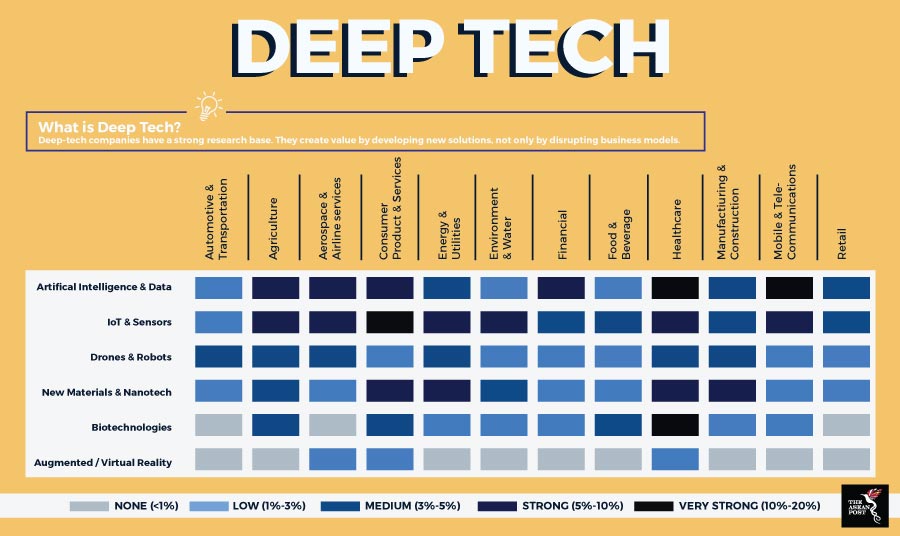 Source: Various sources
Source: Various sources
AI: Leading us into the future
Perhaps the most revolutionary technology which has seen budding application in modern life is AI.
Leading the AI charge in the Southeast Asian startup scene is Glueck. The Malaysian based startup develops sophisticated computer vision, AI and deep machine learning algorithms to assess responses to stimuli in real time environments. The product suite offers tools which can collect information on audiences’ facial elements, age, gender and ethnicity, analyse it and provide readings on the measurement of advertisement ROI (return on investment) so that advertisers can better evaluate their advertising broadcast.
AI is also being used by Filipino infotainment platform, Ad Mov. It is quite literally a tablet PC placed in Grab cars to target advertisements to passengers, especially those who are stuck in Manila’s infamous traffic snarls. By way of the camera on the tablet PC, the AI technology kicks in to identify the age and gender of the passenger and subsequently shows relevant content and ads.
Singaporean based ViSenze has found a novel way of applying AI in e-commerce. Using an AI powered visual search, consumers can simply select or click an image on their device, and the ViSenze API analyses the image and returns similar items which are available for sale on e-commerce platforms. In essence, it helps convert any visual display into an engagement opportunity, shortening the path of action it takes for consumers to purchase a product.
Research driven solutions
Big Data analytics is an increasingly integral part of the tech ecosystem. The ability to transform raw data into meaningful insights is the cornerstone of app and platform development. Indian based Scalend which has offices in Malaysia and Singapore has been developing big data solutions which can handle a variety of data sources – structured, unstructured or semi structured – and of any volume. The platform has a data transformation workbench, with a provision to join data from multiple systems. It also includes capabilities around filtering and data cleansing to bring together meaningful data. The in-built modelling infrastructure also provides over 700 industry standard mathematical and statistical functions and algorithms for predictive and prescriptive insights.
Robotics is also a fast-developing area and Vietnam based Robot3T has grown to become one of the region’s leading research and manufacturing groups in robotics and automation. They perform research on a wide variety of related topics including semiconductor robots, medical robots, human-robot interaction and robot exoskeletons. Their hardware and software products, ranging from tool automation modules and associated controls to complete integration solutions, are designed to work together efficiently, and to support industry standards.
This article was first published by The ASEAN Post on 23 April 2018 and has been updated to reflect the latest data.
Related articles:
How disruptive technologies are transforming Southeast Asia
Regulating artificial intelligence adoption in Southeast Asia
The prospect of AI in Southeast Asia
